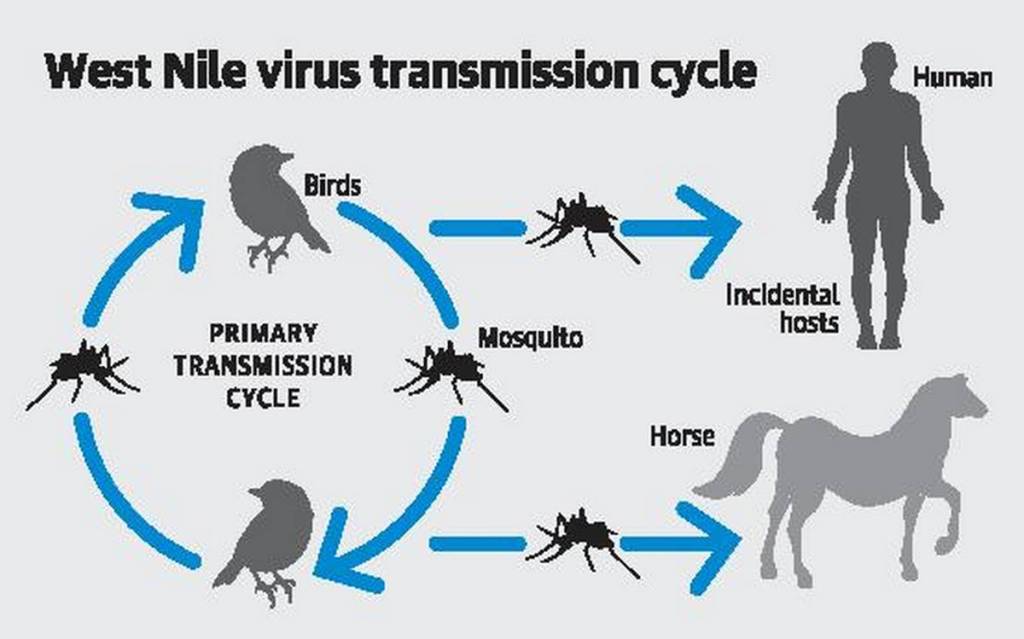
West Nile infection (WNV) is a solitary abandoned RNA infection that causes West Nile fever. It is an individual from the family Flaviviridae, explicitly from the sort Flavivirus, which additionally contains the Zika infection, dengue infection, and yellow fever infection. West Nile infection is basically communicated by mosquitoes, generally types of Culex. The essential hosts of WNV are winged animals, so the infection stays inside a “fledgling mosquito–fowl” transmission cycle.
Structure
Like most different flaviviruses, WNV is a wrapped infection with icosahedral symmetry. Image reproductions and cryoelectron microscopy uncover a 45–50 nm virion covered with a moderately smooth protein shell; this structure is like the dengue fever infection, another Flavivirus. The protein shell is made of two basic proteins: the glycoprotein E and the little film protein M. Protein E has various capacities including receptor authoritative, viral connection, and passage into the cell through layer fusion.
The external protein shell is covered by a host-inferred lipid film, the viral envelope. The flavivirus lipid layer has been found to contain cholesterol and phosphatidylserine, however different components of the film still can’t seem to be identified. The lipid film has numerous functions in viral contamination, including going about as flagging atoms and improving section into the cell. Cholesterol, specifically, has a fundamental impact in WNV entering a host cell. The two viral envelope proteins, E and M, are embedded into the membrane.
The RNA genome is bound to capsid (C) proteins, which are 105 amino-corrosive buildups long, to shape the nucleocapsid. The capsid proteins are one of the principal proteins made in a tainted cell; the capsid protein is a basic protein whose primary design is to bundle RNA into the creating viruses. The capsid has been found to forestall apoptosis by influencing the Akt pathway.
Genome
WNV is a positive-sense, single-abandoned RNA infection. Its genome is around 11,000 nucleotides in length and is flanked by 5′ and 3′ non-coding stem circle structures. The coding area of the genome codes for three basic proteins and seven nonstructural (NS) proteins, proteins that are not consolidated into the structure of new infections. The WNV genome is first converted into a polyprotein and later divided by infection and host proteases into isolated proteins (for example NS1, C, E).
Structural Proteins
Basic proteins (C, prM/M, E) are capsid, antecedent film proteins, and envelope proteins, respectively. The basic proteins are situated at the 5′ end of the genome and are severed into develop proteins by both host and viral proteases.
| Structural Protein | Function |
| C | Capsid protein; encases the RNA genome, bundles RNA into youthful virions. |
| prM/M | Infections with M protein are irresistible: the presence of M protein considers the enactment of proteins engaged with viral passage into the cell. prM (antecedent layer) protein is available on juvenile virions, by additional cleavage by furin to M protein, the virions become infectious. |
| E | A glycoprotein that frames the viral envelope, ties to receptors on the host cell surface to enter the cell. |
Nonstructural proteins
Nonstructural proteins comprise of NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS5. These proteins basically help with viral replication or go about as proteases. The nonstructural proteins are situated close to the 3′ end of the genome.
| Nonstructural Protein | Function |
| NS1 | NS1 is a cofactor for viral replication, explicitly for guideline of the replication complex. |
| NS2A | NS2A has an assortment of capacities: it is associated with viral replication, virion gathering, and inciting host cell death. |
| NS2B | A cofactor for NS3 and together structures the NS2B-NS3 protease complex. Contains transmembrane areas which tie the protease to intracellular layers. |
| NS3 | A serine protease that is liable for separating the polyprotein to deliver develop proteins; it likewise goes about as a helicase. |
| NS4A | NS4A is a cofactor for viral replication, explicitly controls the action of the NS3 helicase. |
| NS4B | Represses interferon signaling. |
| NS5 | The biggest and most moderated protein of WNV, NS5 goes about as a methyltransferase and a RNA polymerase, however it needs editing properties. |
Life Cycle
When WNV has effectively entered the circulation system of a host creature, the envelope protein, E, ties to connection factors called glycosaminoglycans on the host cell.[16] These connection factors help passage into the phone, nonetheless, official to essential receptors is likewise necessary. Primary receptors incorporate DC-SIGN, DC-SIGN-R, and the integrin αvβ3.By authoritative to these essential receptors, WNV enters the phone through clathrin-interceded endocytosis. because of endocytosis, WNV enters the phone inside an endosome.
The sharpness of the endosome catalyzes the combination of the endosomal and viral films, permitting the genome to be delivered into the cytoplasm. Translation of the positive-sense single-abandoned RNA happens at the endoplasmic reticulum; the RNA is converted into a polyprotein which is then divided by both host and viral proteases NS2B-NS3 to create develop proteins.
To duplicate its genome, NS5, a RNA polymerase, frames a replication complex with other nonstructural proteins to create a delegate negative-sense single-abandoned RNA; the negative-sense strand fills in as a layout for combination of the last certain sense RNA. Once the positive-sense RNA has been integrated, the capsid protein, C, encases the RNA strands into youthful virions. The remainder of the infection is gathered along the endoplasmic reticulum and through the Golgi contraption, and results in non-irresistible juvenile virions. The E protein is then glycosylated and prM is separated by furin, a host cell protease, into the M protein, in this way delivering an irresistible develop virion. The develop infections are then emitted out of the phone.
Phylogeny
WNV is one of the Japanese encephalitis antigenic serocomplex of infections, along with Japanese encephalitis infection, Murray Valley encephalitis infection, Saint Louis encephalitis infection and some other flaviruses. Studies of phylogenetic ancestries have confirmed that WNV arose as an unmistakable infection around 1000 years ago. This underlying infection formed into two particular genealogies. Ancestry 1 and its numerous profiles is the wellspring of the scourge transmission in Africa and all through the world. Heredity 2 was viewed as an African zoonosis. Notwithstanding, in 2008, ancestry 2, already just found in ponies in sub-Saharan Africa and Madagascar, started to show up in ponies in Europe, where the main realized flare-up influenced 18 creatures in Hungary. Lineage 1 West Nile infection was recognized in South Africa in 2010 out of a horse and her prematurely ended hatchling; beforehand, just genealogy 2 West Nile infection had been identified in ponies and people in South Africa. Kunjin infection is a subtype of West Nile infection endemic to Oceania. A 2007 lethal case in a stellar whale in Texas widened the realized host scope of West Nile infection to incorporate cetaceans.
Since the main North American cases in 1999, the infection has been accounted for all through the United States, Canada, Mexico, the Caribbean, and Central America. There have been human cases and equine cases, and numerous winged animals are tainted. The Barbary macaque, Macaca sylvanus, was the main nonhuman primate to contract WNV. Both the American and Israeli strains are set apart by high death rates in contaminated avian populaces; the presence of dead flying creatures—particularly Corvidae—can be an early pointer of the appearance of the infection.
Host Range & Transmission
The normal hosts for WNV are feathered creatures and mosquitoes. Over 300 unique types of fowl have been demonstrated to be tainted with the virus. Some winged animals, including the American crow (Corvus brachyrhynchos), blue jay (Cyanocitta cristata) and more prominent sage-grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus), are murdered by the contamination, however others survive. The American robin (Turdus migratorius) and house sparrow (Passer domesticus) are believed to be among the main repository species in N. American and European cities. Brown thrashers (Toxostoma rufum), dim catbirds (Dumetella carolinensis), northern cardinals (cardinalis), northern mockingbirds (Mimus polyglottos), wood thrushes (Hylocichla mustelina) and the bird family are among the other regular N. American feathered creatures in which significant levels of antibodies against WNV have been found.
WNV has been shown in countless mosquito species, yet the most critical for viral transmission are Culex species that feed on winged creatures, including Culex pipiens, C. restuans, C. salinarius, C. quinquefasciatus, C. nigripalpus, C. erraticus and C. tarsalis. Experimental contamination has additionally been exhibited with delicate tick vectors, however is probably not going to be significant in common transmission.
WNV has a wide host range, and is additionally known to have the option to contaminate in any event 30 mammalian species, including people, some non-human primates, ponies, canines and cats. Some tainted people and ponies experience sickness however canines and felines seldom show symptoms. Reptiles and creatures of land and water can likewise be contaminated, including a few types of crocodiles, gators, snakes, reptiles and frogs. Mammals are viewed as accidental or impasse has for the infection: they don’t generally build up a sufficiently high degree of infection in the blood (viremia) to contaminate another mosquito benefiting from them and carry on the transmission cycle; a few winged animals are likewise impasse hosts.
In the typical rustic or enzootic transmission cycle, the infection switches back and forth between the flying creature store and the mosquito vector. It can likewise be communicated between fowls by means of direct contact, by eating a tainted flying creature body or by drinking contaminated water. Vertical transmission among female and posterity is conceivable in mosquitoes, and may possibly be significant in overwintering. In the metropolitan or overflow cycle, tainted mosquitoes that have benefited from tainted winged animals send the infection to people. This requires mosquito species that nibble the two fowls and people, which are named connect vectors. The infection can likewise infrequently be spread through blood bondings, organ transfers, or from mother to infant during pregnancy, conveyance, or breastfeeding. Unlike in flying creatures, it doesn’t in any case spread straightforwardly between people.
Disease
Humans
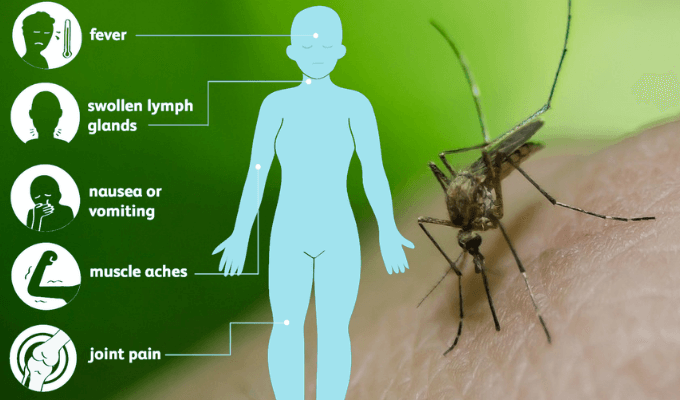
In people, West Nile infection can cause a sickness known as West Nile fever. According to the U.S. Habitats for Disease Control and Prevention, roughly 80% of contaminated individuals have not many or no symptoms, around 20% of individuals create mellow manifestations, (for example, fever, cerebral pain, regurgitating, or a rash), and under 1% of individuals create extreme indications, (for example, encephalitis or meningitis with related neck solidness, disarray, or seizures). The reasons for West Nile Virus intervened encephalitis have been investigated by Dr. Robyn Klein at Washington University in St. Louis. She has discovered that West Nile contamination builds cytokines and chemokines in the blood, making the blood mind boundary more defective and defenseless to infection. The danger of death among patients with sensory system indications is about 10%. Recovery may take a long time to months. Risks for serious sickness incorporate age more than 60 and other wellbeing problems. Historically, individuals in territories where the infection was endemic, for example, the Nile Delta, normally experienced subclinical or mellow disease. Diagnosis is commonly founded on manifestations and blood tests. While there is no particular therapy, torment meds might be useful.
Horses
Extreme sickness may likewise happen in horses. Several immunizations for these creatures are currently available. Before the accessibility of veterinary antibodies, around 40% of ponies contaminated in North America died.
History
The infection was found in Uganda in 1937 and was first recognized in North America in 1999.
West Nile Virus has been accounted for in Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia, and North America. In the United States a great many cases are accounted for a year, with most happening in August and September. It can happen in flare-ups of disease. A reconnaissance framework in flying creatures is helpful for early location of a potential human outbreak.
Epidemiology
As per the Center for Disease Control, contamination with West Nile Virus is occasional in mild zones. Atmospheres that are mild, for example, those in the United States and Europe, see top season from July to October. Pinnacle season changes relying upon geographic district and hotter and damp atmospheres can see longer top seasons. All ages are similarly liable to be contaminated yet there is a higher measure of death and neuroinvasive West Nile Virus in individuals 60-89 years old. People of more established age are bound to have unfriendly impacts of being tainted.
There are a few methods of transmission however the most well-known reason for disease in people is by being nibbled by a contaminated mosquito. Different methods of transmission incorporate blood bonding, organ transplantation, bosom taking care of, transplacental transmission, and research center obtaining. These elective methods of transmission are amazingly rare.
Prevention
Avoidance endeavors against WNV predominantly center around forestalling human contact with and being chomped by tainted mosquitoes. This is twofold, first by close to home defensive activities and second by mosquito-control activities. At the point when an individual is in a region that has WNV, it is essential to evade open air action, and in the event that they go outside they should utilize a mosquito repellent with DEET. An individual can likewise wear dress that covers more skin, for example, long sleeves and jeans. Mosquito control should be possible at the network level and incorporate reconnaissance projects and control programs including pesticides and diminishing mosquito living spaces. This incorporates depleting standing water. Observation frameworks in winged animals is especially useful. If dead flying creatures are found in a local it should report it to neighborhood specialists. This may help wellbeing divisions do observation and decide whether the flying creatures are contaminated with West Nile Virus.
Regardless of the business accessibility of four veterinary antibodies for ponies, no people immunization has advanced past stage II clinical trials. Efforts have been made to deliver an immunization for human use and a few competitors have been created yet none are authorized to use.The best strategy to lessen the danger of diseases is dodging mosquito bites. This might be finished by taking out standing pools of water, for example, in old tires, basins, drains, and swimming pools. Mosquito repellent, window screens, mosquito nets, and evading territories where mosquitoes happen may likewise be useful.