Yersinia enterocolitica is a Gram-negative, bacillus-formed bacterium, having a place with the family Yersiniaceae. It is motile at temperatures of 22–29°C (72–84°F), yet gets nonmotile at ordinary human body temperature. Y. enterocolitica contamination causes the infection yersiniosis, which is a creature borne sickness happening in people, just as in a wide exhibit of creatures, for example, cows, deer, pigs, and fowls. Huge numbers of these creatures recuperate from the illness and become transporters; these are likely wellsprings of virus notwithstanding giving no indications of disease. The bacterium taints the host by adhering to its phones utilizing trimeric autotransporter adhesins.
The variety Yersinia incorporates 20 species: Y. aldovae, Y. aleksiciae, Y. bercovieri, Y. canariae, Y. enterocolitica, Y. entomophaga, Y. frederiksenii, Y. hibernica, Y. intermedia, Y. kristensenii, Y. massiliensis, Y. mollaretii, Y. nurmii, Y. pekkanenii, Y. pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, Y. rohdei, Y. ruckeri, Y. similis, and Y. wautersii. Among them, just Y. pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and certain strains of Y. enterocolitica are of pathogenic significance for people and certain warm-blooded creatures, while different species are of ecological birthplace and may, best case scenario, go about as go getters. In any case, Yersinia strains can be disconnected from clinical materials, so they must be distinguished at the species level.
Y. enterocolitica is a heterogeneous gathering of strains, which are customarily characterized by biotyping into six biogroups based on phenotypic qualities, and by serotyping into in excess of 57 O serogroups, based on their O (lipopolysaccharide or LPS) surface antigen. Five of the six biogroups (1B and 2–5) are viewed as microorganisms. In any case, a couple of these serogroups have been related with infection in one or the other people or creatures. Strains that have a place with serogroups O:3 (biogroup 4), O:5,27 (biogroups 2 and 3), O:8 (biogroup 1B), and O:9 (biogroup 2) are most often disconnected worldwide from human examples. Be that as it may, the main Y. enterocolitica serogroup in numerous European nations is serogroup O:3 followed by O:9, while the serogroup O:8 is fundamentally identified in the United States.
Y. enterocolitica is broad in nature, happening in supplies going from the intestinal plots of various vertebrates, avian species, cutthroat species, and even from earthbound and oceanic specialties. Most natural disengages are avirulent; notwithstanding, separates recuperated from porcine sources contain human pathogenic serogroups. Furthermore, canines, sheep, wild rodents, and ecological water may likewise be a supply of pathogenic Y. enterocolitica strains. Human pathogenic strains are generally bound to the intestinal lot and lead to enteritis/diarrhea.
Signs & Symptoms
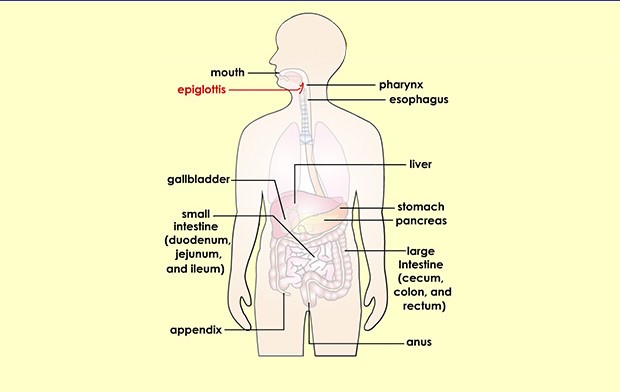
The gateway of section is the gastrointestinal parcel. The creature is obtained typically by inadequately cooked pork or defiled water, meat, or milk. Intense Y. enterocolitica diseases typically lead to mellow self-restricting enterocolitis or terminal ileitis and adenitis in people. Indications may incorporate watery or bleeding the runs and fever, taking after an infected appendix or salmonellosis or shigellosis. After oral take-up, Yersinia species recreate in the terminal ileum and attack Peyer’s patches. From here they can spread further to mesenteric lymph hubs causing lymphadenopathy. This condition can be mistaken for a ruptured appendix, so is called pseudoappendicitis. In immunosuppressed people, they can spread from the gut to the liver and spleen and structure abscesses. Since Yersinia species are siderophilic (iron-cherishing) microbes, individuals with innate hemochromatosis (an illness bringing about high body iron levels) are more vulnerable to contamination with Yersinia (and other siderophilic microorganisms). Truth be told, the most well-known pollutant of put away blood is Y. enterocolitica. See yersiniosis for additional subtleties.
Treatment
Yersiniosis is typically self-restricting and doesn’t need treatment. For sepsis or extreme central contaminations, particularly whenever related with immunosuppression, the suggested routine remembers doxycycline for blend with an aminoglycoside. Different anti-toxins dynamic against Y. enterocolitica incorporate trimethoprim-sulfamethoxasole, fluoroquinolones, ceftriaxone, and chloramphenicol. Y. enterocolitica is normally impervious to penicillin G, ampicillin, and cefalotin because of beta-lactamase production.
Prognosis
Y. enterocolitica contaminations are now and again followed by constant provocative infections, for example, arthritis, erythema nodosum, and responsive joint pain. This is doubtlessly a direct result of some insusceptible interceded mechanism.
Y. enterocolitica is by all accounts related with immune system Graves-Basedow thyroiditis. Whilst backhanded proof exists, direct causative proof is limited. Y. enterocolitica is most likely not a significant reason for this sickness, but rather may add to the advancement of thyroid autoimmunity emerging for different reasons in hereditarily powerless individuals. Y. enterocolitica contamination has additionally been recommended to be not the reason for immune system thyroid sickness, but instead a related condition, with both sharing a typical acquired susceptibility. More as of late, the function for Y. enterocolitica has been disputed.